안녕하세요 버섯돌이 유재성입니다.
Wifi-Direct를 시간이되면 공부하려고 했었는데 카페에 좋은 링크가 있어서 잊어 버리기전에 살짝 퍼다 나릅니다.
Wifi-Direct는 의미 그대로 인터넷(?)이 할당되지 않아도 p2p처럼 해당 와이파이에 직접 접속하는 기술을 의미합니다.
기존의 공유기들도 펌웨어 업데이트에 의해 가능한것으로 알고있고, 안드로이드에서는 4.X대 이상의 OS에서만 지원 하는데
폰 제조사와 버전별로 사용 방법은 다른걸로 알고 있습니다.
쉽게 생각해서 카메라가 Wifi-Direct를 제공하고 스마트폰도 Wifi-Direct를 제공한다면...
인터넷이 안되는 외부에서 AP없이 카메라와 스마트폰을 서로 직접 연결해서 데이터 전송이 가능해집니다.
장점으로는 Wifi-Direct는 블루투스 4보다도 송/수신 거리가 2배나 길어서 200미터까지 전송 가능하며 300Mbps입니다.
라즈베리 파이가 USB포트가 있어서 나중에 차량같은거 만들면 라즈베리 파이에 적용해 보려고 생각만 하고 있었습니다.^^;;;
ㅎㅎ..저도 안 해 봤으니 질문은 사절~~~ 영어되시는 분은 번역 환영~ 관련 강좌글 환영~~*^_^*V
출처 : http://dishingtech.blogspot.kr/2012/01/realtek-wi-fi-direct-programming-guide.html
Realtek Wi-Fi Direct Programming Guide
Wi-Fi Direct (P2P) is the new technology developed by Wi-Fi Alliance. Wi-Fi Direct is a solution for Wi-Fi device-to-device connectivity. And it is also backward compatible with existing Wi-Fi Certified devices. The following picture is the overview for Wi-Fi Direct architecture of Realtek Linux Wi-Fi Direct software. “User Interface App (UI)” is an application which should be designed by customer for their product. UI should use the iwpriv application to get / set whole the P2P information from/to the Realtek Wi-Fi driver.
Iwpriv application is available in the wpa_supplicant_hostapd folder and we also provide the porting guide under document folder.
(Please refer to the Wireless_tools_porting_guide.pdf) Of course, the UI can use the iwpriv application to issue the P2P information to driver based on the Wi-Fi Direct APIs described in this document.
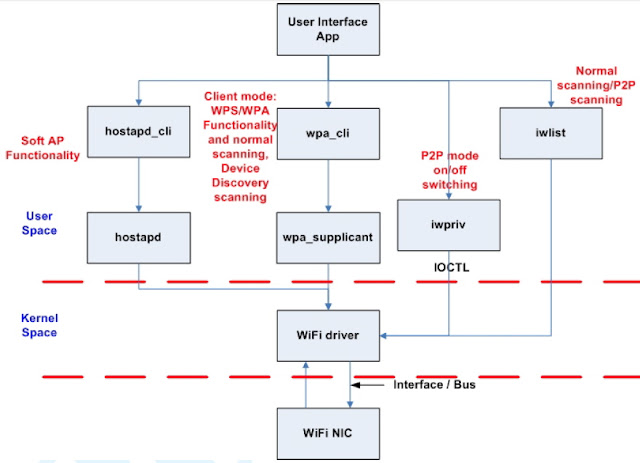 |
| Figure 1: Software Architecture for Realtek Linux Wi-Fi Direct |
wpa_cli and wpa_supplicant are the standard application to handle whole the 802.11 station mode connection. Hostapd and hostapd_cli are also the standard application to handle whole the 802.11 AP mode connections.
In usual, there are 4 stages in the Wi-Fi Direct scenario.
1. “Device Discovery”
2. “Provision Discovery”
3. “Group Formation”
4. “Provisioning”
The following picture will provide the overall concept for Wi-Fi Direct functionality and it will also contain these 4 stages described above.
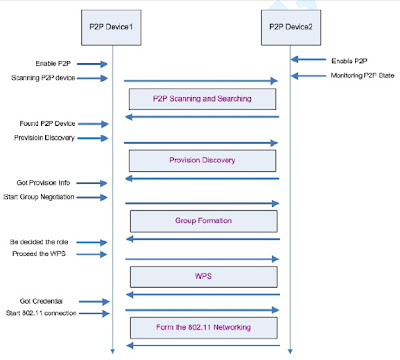 |
| Figure 2: Wi-Fi Direct Overview |
Figure 2 describes the basic Wi-Fi Direct scenario and this document will use this figure to explanation the Wi-Fi Direct functionality and APIs.
1. Enable P2P
In this case, there are two Wi-Fi devices which both support the Wi-Fi Direct
functionality. We can use the iwpriv to enable the Wi-Fi Direct function of Realtek Wi-Fi driver (enable P2P).
#> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set enable=n
“wlan0” is the network interface for Realtek Wi-Fi device on the system.
“p2p_set” command is used to pass the settings information to the driver.
“enable” is the actual command to tell the driver which information the application is trying to set. “n” is a number to set the P2P functionality.
“n=0” means to disable the P2P functionality
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set enable=0
“n=1” means to turn the P2P functionality on and the Wi-Fi driver will be the P2P device mode.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set enable=1
“n=2” means to turn the P2P functionality on and the Wi-Fi driver will be the
P2P client mode.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set enable=2
“n=3” means to turn the P2P functionality on and the Wi-Fi driver will be the
P2P group owner mode.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set enable=3
“n” had been defined in the P2P.h file of the document folder. This document also copies that definition here for the reference.
enum P2P_ENABLEINFO {
P2P_DISABLE = 0,
P2P_ENABLE_WITH_DEVICE = 1,
P2P_ENABLE_WITH_CLIENT = 2,
P2P_ENABLE_WITH_GO = 3,
};
2. Scanning P2P Device
After enabling the P2P functionality of the Wi-Fi driver, the P2P device1 got to find out how many other P2P devices exist in the environment. The UI can do the scan via wpa_supplicant or iwlist command.
For wpa_supplicant:
Ex: #> wpa_cli scan // Ask wpa_supplicant to do the scanning
Ex: #> wpa_cli scan_results // Get the scanning result
For iwlist:
Ex: #> iwlist wlan0 scan// Issue the scanning request to driver and result the scanning result.
When enabling the P2P functionality of the Wi-Fi driver, the Wi-Fi driver will just provide the device lists which support the Wi-Fi Direct. If the UI wants to list all the 802.11 network when doing the scanning, the UI can use the “iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set enable=0” command to disable the P2P functionality and re-do the scanning.
3. Provision Discovery
The purpose for the provision discovery is to get the WPS Pin Code or WPS push button for the following WPS procedure.
“prov_disc” is the command to start the provision procedure.
“00:11:22:33:44:55” is the MAC address of peer P2P device (P2P Device2 in the Figure 2) which you want to get the WPS information. “_” is a connector.
“display” means the peer P2P device should display its PIN CODE on its screen and the user should key-in this PIN CODE on the local P2P device (P2P Device1 in Figure 1). “keypad” means the local P2P device should display its PIN CODE on its screen and the user should key-in this PIN CODE on the peer P2P device. “pbc” means these two P2P device will use the WPS push button for the following WPS procedure. “label” means the user should read the PIN CODE from the label of peer P2P device and key-in this PIN CODE of this label on the local P2P device. And now, both local P2P device and peer P2P device had got the PIN CODE or PBC and should be ready to form an 802.11 network.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set prov_disc=00:11:22:33:44:55_display
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set prov_disc=00:11:22:33:44:55_keypad
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set prov_disc=00:11:22:33:44:55_pbc
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set prov_disc=00:11:22:33:44:55_label
After getting the WPS PIN CODE or PBC, the UI should use the “got_wpsinfo” command to inform the Wi-Fi driver for this.
“got_wpsinfo=1” means the UI got the WPS PIN CODE from peer P2P device’s screen or label and uses key-in this PIN CODE on the local P2P device.
“got_wpsinfo=2” means the PIN CODE is displayed from the local P2P device and user had key-in this PIN CODE on the peer P2P device.
“got_wpsinfo=3” means the UI got the WPS PBC.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set got_wpsinfo=1
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set got_wpsinfo=2
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set got_wpsinfo=3
The P2P.h file also defined the value and meaning for the “got_wpsinfo” command.
enum P2P_WPSINFO {
P2P_NO_WPSINFO = 0,
P2P_GOT_WPSINFO_PEER_DISPLAY_PIN = 1,
P2P_GOT_WPSINFO_SELF_DISPLAY_PIN = 2,
P2P_GOT_WPSINFO_PBC = 3,
};
On the P2P device2 side of Figure 2, it can use the “status” command to check the current P2P state. If the status string is the “Status=08”, it means the driver received the provision discovery request from certain P2P device. At this moment, the UI should use the “req_cm” command to know which WPS method the certain P2P device is purpose to do.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_get req_cm
Return String:
CM=dis
or
CM=lab
or
CM=pbc
or
CM=pad
If the return string is “CM=dis”, it means the peer P2P device want to this P2P device to show up the PIN CODE on the local screen so that the user can key-in this PIN CODE on the peer P2P device.
If the return string is “CM=lab”, it means the peer P2P device want to use the PIN CODE printed on the label of this P2P device and user can key-in this PIN CODE on the peer P2P device. If the return string is “CM=pbc”, it means the peer P2P device wants to use the PBC for the following WPS procedure.
If the return string is “CM=pad”, it means the peer P2P device will show its PIN CODE on the peer P2P device side and the user should key-in this PIN CODE on the local P2P device.
4. Start Group Negotiation
In the Wi-Fi Direct scenario, one of the P2P devices will become a group owner (SoftAP) and the other P2P device will become an 802.11 client to connect to the SoftAP. The stage4 “Start Group Negotiation” is the procedure to determine which P2P device should be the group owner/client.
“intent” is a value from 0 ~ 15. This value will provide the degree information to want to be the group owner. “intent=15” means this Wi-Fi driver must be the group owner. The default intent value is 1 and this default value will be assigned by enabling the P2P functionality.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set intent=n
Beside the intent value, the UI should determine the SSID which will be used when this P2P device becomes the group owner with SoftAP functionality in the future. After UI determine the SSID, the UI should pass that SSID to the driver by using the ssid command. This information must be passed to driver before calling the “nego” command.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set ssid=SsidString
“nego” command will inform the Wi-Fi driver to perform the group negotiation procedure.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_set nego=00:11:22:33:44:55
In Figure 2, the P2P Device2 is using the “status” and “role” commands to monitor the P2P state machine so that the UI of P2P Device2 just is able to know what kinds of information the P2P Device1 sent.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_get status
Return string :
Status=02
or
Status=10
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_get role
Return string: Role=01
The following two enum are the definition for the “status” and “role” commands.
enum P2P_STATE {
P2P_STATE_NONE = 0, // P2P disable
P2P_STATE_IDLE = 1, // P2P had enabled and do nothing
P2P_STATE_LISTEN = 2, // In pure listen state
P2P_STATE_SCAN = 3, // In scan phase
P2P_STATE_FIND_PHASE_LISTEN = 4, // In the listen state of find phase
P2P_STATE_FIND_PHASE_SEARCH = 5, // In the search state of find phase
P2P_STATE_TX_PROVISION_DIS_REQ = 6,// In P2P provisioning discovery
P2P_STATE_RX_PROVISION_DIS_RSP = 7,
P2P_STATE_RX_PROVISION_DIS_REQ = 8,
P2P_STATE_GONEGO_ING = 9, // Doing the group owner negoitation handshake
P2P_STATE_GONEGO_OK = 10, // finish the group negoitation handshake with success
P2P_STATE_GONEGO_FAIL = 11,// finish the group negoitation handshake with failure
P2P_STATE_RECV_INVITE_REQ = 12,// receiving the P2P Inviation request
P2P_STATE_PROVISIONING_ING = 13, // Doing the P2P WPS
P2P_STATE_PROVISIONING_DONE = 14, // Finish the P2P WPS
};
enum P2P_ROLE {
P2P_ROLE_DISABLE = 0,
P2P_ROLE_DEVICE = 1,
P2P_ROLE_CLIENT = 2,
P2P_ROLE_GO = 3
};
For example, the UI of P2P Device2 will get the “Status=08” when the P2P Device1 proceeds the Provision Discovery procedure.
“State=10” means the group negotiation procedure is finished with success.
“State=11” means the group negotiation procedure is finished with failure.
After the P2P Device1 and P2P Device2 found the group negotiation finished, they can use the “role” command to know the role they should play in the following operation.
Ex: #> iwpriv wlan0 p2p_get role
Return string: Role=02
If the return string is “Role=02”, it means this P2P device should play the 802.11 client role in the following operation. The UI should launch wpa_supplicant to perform the WPS procedure with the peer P2P device.
If the return string is “Role=03”, it means this P2P device should be the 802.11
AP role in the following operation. The UI should launch the hostapd to enable the SoftAP functionality and enable the WPS procedure.
5. Proceed the WPS
After confirming the role for both P2P Device1 and P2P Device2, the P2P device which got the“Role=02” should launch the wpa_supplicant in the background and use the wpa_cli with PIN CODE or PBC to perform the WPS procedure.
In the same word, the P2P device which got the “Role=03” should launch the hostapd in the background and use the hostapd_cli with PIN CODE or PBC to perform the WPS procedure. (Please refer to Quick_Start_Guide_for_SoftAP.pdf for further information.)
6. DHCP
The Wi-Fi Direct Specification required that the P2P device which becomes the group owner should also provide the DHCP server application in their system. The DHCP server should be launched and be ready to provide the IP address to the DHCP client. The specification also required that the P2P device which becomes the P2P client should launch the DHCP client application to acquire the IP address from the P2P group owner after the wpa_supplicant established the 802.11 connection with AP successfully.
Realtek Drivers (Linux / Win / Mac)

